Hey there, developers! Today I want to talk about an astonishing .NET library called Mapperly, which has been gaining much attention in the developer community. Mapperly is a powerful source generator that simplifies the implementation of object-to-object mappings in .NET applications. Mapperly takes mapping to a whole new level by generating mapping code for you based on the mapping method signatures you define.
If you’re tired of writing repetitive mapping code and seeking a seamless solution to simplify object mappings in your .NET projects, Mapperly is the answer you’ve been waiting for. Join me in this blog post to learn more!
You got my attention, tell me more
One of the remarkable advantages of using Mapperly is that it generates the mapping code at build time, resulting in minimal runtime overhead. This means your application runs smoothly without any performance compromises. Plus, the generated code is incredibly readable, allowing you to easily understand and verify the mapping logic behind the scenes.
Mapperly leverages the capabilities of .NET Source Generators, avoiding the need for runtime reflection. This not only makes the generated code highly optimized but also ensures compatibility with Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation and trimming. Your application remains efficient and maintains excellent performance.
Notably, Mapperly is known for being one of the fastest .NET object mappers available. In fact, it even surpasses the traditional manual mapping approach in terms of speed and efficiency. These exceptional performance benchmarks have been verified using Benchmark.netCoreMappers.
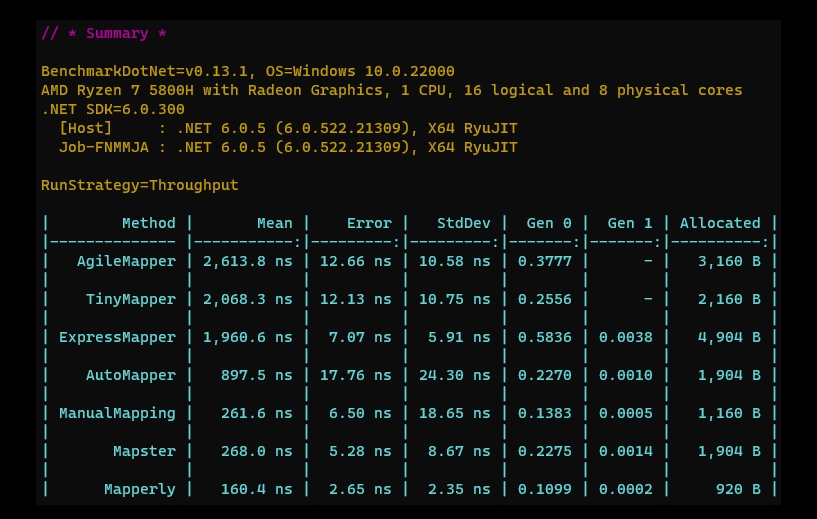
Source: https://github.com/mjebrahimi/Benchmark.netCoreMappers
Getting Started
To install Mapperly, you just need to add a NuGet reference to the Riok.Mapperly package:
dotnet add package Riok.Mapperly
Creating a Mapper: Mapping a Class to a DTO
Now, let’s create a mapper using Mapperly to map a Person class to a PersonDto data transfer object (DTO).
Here’s the Person class definition:
public class Person
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<string> Tags { get; set; }
}
And the corresponding PersonDto class definition:
public class PersonDto
{
public int PersonId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public IReadOnlyCollection<TagDto> Tags { get; set; }
}
public record TagDto(string tag);
Now, let’s create our mapper class, PersonMapper, and define the mapping method PersonToPersonDto. We’ll mark it with the [Mapper] attribute and we will create it as partial:
using Riok.Mapperly.Abstractions;
[Mapper]
public partial class PersonMapper
{
[MapProperty(nameof(Person.Id), nameof(PersonDto.PersonId))] // Map property with a different name in the target type
public partial PersonDto PersonToPersonDto(Person person);
}
Since both Id/PersonId properties are named differently, we added a [MapProperty] to configure the mapping
Generating and Viewing the Mapperly Source Code
Most IDEs provide easy access to the generated code, allowing you to navigate from the partial mapper method to its implementation. However, if your IDE doesn’t support this feature or if you prefer to include the generated source code in your source control, you can emit the generated files to disk.
To emit the generated files to disk, you need to set the EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles property in your project file (.csproj). Here’s how you can do it:
<PropertyGroup>
<EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>true</EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>
</PropertyGroup>
By default, the emitted files are written to {BaseIntermediateOutpath}/generated/{Assembly}/Riok.Mapperly/{GeneratedFile}. The BaseIntermediateOutpath is typically obj/Debug/net7.0.
Once you’ve set up the emitted files, they will be generated during the build process. This allows you to easily access the updated mapper code and mapper diagnostics. It’s worth noting that emitting the files during each build provides better performance in the IDE, preventing potential lagginess.
With the ability to generate and view the source code, you can better understand and analyze the generated mappings. This feature enhances the transparency and maintainability of your codebase. Now let us look into the generated mapping code:
public partial class PersonMapper
{
public partial global::Client.PersonDto PersonToPersonDto(global::Client.Person person)
{
var target = new global::Client.PersonDto();
target.PersonId = person.Id;
target.Name = person.Name;
target.Tags = global::System.Linq.Enumerable.ToArray(global::System.Linq.Enumerable.Select(person.Tags, x => new global::Client.TagDto(x)));
return target;
}
}
Let us examin what happened here.
-
PersonId and Id are mapped since we added the MapProperty attribute
-
Name is automatically mapped since the both properties are the same name
-
Tags property is automatically mapped from IEnumerable
into collection of TagDto
Now, let’s add a few more things to our classes to check the generated mapping code. I’m going to add an enum in both classes, and the target DTO class will have some missing enums and different values. Here, we can see how Mapperly will map it.
The updated Person class
public class Person
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public MartialStatus MartialStatus { get; set; }
public List<string> Tags { get; set; }
}
public enum MartialStatus
{
Undefined = 0,
Married = 1,
Single = 2,
Widowed = 3,
Divorced = 4,
Separated = 5
}
and here is the updated PersonDto class
public class PersonDto
{
public int PersonId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public MartialStatusDto MartialStatus { get; set; }
public IReadOnlyCollection<TagDto> Tags { get; set; }
}
public enum MartialStatusDto
{
Widowed = 10,
Married = 11,
Single = 12
}
public record TagDto(string tag);
Because the MartialStatus and MaritalStatusDto entries have different numeric values, we need to configure Mapperly to map them by their name. To do that, we need to update the [Mapper] attribute as follows:
[Mapper(EnumMappingStrategy = EnumMappingStrategy.ByName)]
public partial class PersonMapper
{
[MapProperty(nameof(Person.Id), nameof(PersonDto.PersonId))]
public partial PersonDto PersonToPersonDto(Person person);
}
Let’s take a look at the generated PersonMapper code:
public partial class PersonMapper
{
public partial global::Client.PersonDto PersonToPersonDto(global::Client.Person person)
{
var target = new global::Client.PersonDto();
target.PersonId = person.Id;
target.Name = person.Name;
target.MartialStatus = MapToMartialStatusDto(person.MartialStatus);
target.Tags = global::System.Linq.Enumerable.ToArray(global::System.Linq.Enumerable.Select(person.Tags, x => new global::Client.TagDto(x)));
return target;
}
private global::Client.MartialStatusDto MapToMartialStatusDto(global::Client.MartialStatus source)
{
return source switch
{
global::Client.MartialStatus.Married => global::Client.MartialStatusDto.Married,
global::Client.MartialStatus.Single => global::Client.MartialStatusDto.Single,
global::Client.MartialStatus.Widowed => global::Client.MartialStatusDto.Widowed,
_ => throw new System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(source), source, "The value of enum MartialStatus is not supported"),
};
}
}
It’s interesting to see that Mapperly generates a new method, MapToMarialStatusDto, which uses a switch case to map MartialStatus into MaritalStatusDto.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mapperly is a powerful .NET tool that automates object mapping code generation. It streamlines the mapping process, improves code maintainability, and saves developers time and effort. Embrace Mapperly’s simplicity and efficiency to optimize object mappings in your .NET projects.
Happy mapping with Mapperly!